Kamala Harris vs Donald Trump: Who Will Be a Better President for Africa-US Relations?


Recent polls have revealed a surprising tie between U.S. presidential candidates Kamala Harris and Donald Trump. Harris and Trump are neck and neck, each with 46% support among registered voters. This close race highlights the importance of their differing views on African foreign policy and its effects on U.S.-Africa relations.
Africa’s population is set to exceed 2.5 billion by 2050, making it a crucial player in global affairs. However, the U.S. has historically been less engaged with Africa, ranking second in the Lowy Institute’s Diplomacy Index. This underinvestment in diplomatic efforts raises questions about future economic and security ties with Africa.
ALSO READ: DISCUSSION: Is Donald Trump Good For Africa?
The approaches of Harris and Trump to Africa are starkly different, reflecting in their support bases. Harris garners strong support from younger voters, Black voters, and those with higher education. Trump, on the other hand, enjoys a lead among older and White voters. These demographic differences could profoundly influence U.S.-Africa relations, affecting trade, aid, and diplomatic strategies.
Key Takeaways
- Harris and Trump are virtually tied in recent polls for the U.S. presidency
- Africa’s population is projected to reach 2.5 billion by 2050
- The U.S. ranks high in diplomacy but lacks engagement with Africa
- Harris performs better among younger and diverse voters
- Trump leads among older and White voters
- The election outcome could reshape U.S.-Africa relations
The Current State of US-Africa Relations
US-Africa relations have undergone significant changes, influencing economic growth and global leadership. Africa’s role in American foreign policy has varied, often relegated after the Cold War era. Yet, the relationship remains crucial for both regions.
Historical Context of US Engagement with Africa
The United States has been a dominant force in African affairs. It stands as the largest single donor, providing $9.5 billion in humanitarian aid to Africa in 2023. This aid mainly supports “soft” projects, such as education and health, rather than infrastructure.
Recent Developments in US-Africa Diplomacy
Recent shifts have marked US-Africa relations. The African Growth and Opportunity Act (AGOA) grants tariff-free access to US markets for eligible African countries, enhancing trade. Yet, China has become a formidable competitor, investing $25.7 billion in African infrastructure in 2018, vastly outpacing the US’s $297 million.
Key Challenges Facing US-Africa Relations
Challenges currently affect Africa-US relations. These include:
- Balancing infrastructure investment with China’s growing influence
- Addressing conflicts and insurgencies across the continent
- Promoting human rights while maintaining strategic partnerships
- Adapting to changing global leadership dynamics
The 2024 US presidential election may alter US-Africa relations, with potential shifts in foreign policy priorities under new leadership.
Vice President Kamala Harris’s Africa Engagement: Promise and Pushback
Kamala Harris, the first woman and person of color to become Vice President of the United States, represents a pivotal moment in American politics. Her parents, an Indian mother and a Jamaican father, have shaped her unique cultural identity. This blend of heritage marks a shift in the American political landscape, underscoring the complexities of racial identity.
Her path to the White House was marked by her experiences as a woman of color. At Howard University, a historically Black institution, she developed her leadership skills and deepened her connection to African American culture. This background has significantly influenced her policy-making and diplomatic approach, especially towards Africa.
In 2023, Harris embarked on a tour of Africa, visiting Ghana, Tanzania, and Zambia. Her visit aimed to reset America’s approach to the continent, emphasizing partnerships and collaboration over traditional aid models.
“My mother would look at me and she’d say, ‘Kamala, you may be the first to do many things, but make sure you are not the last.'”
Harris’s Vision for U.S.-Africa Relations
Harris focused on several key areas during her trip:
- Economic partnerships and investment
- Youth empowerment and innovation
- Democracy and good governance
- Climate change and digital inclusion
The Vice President’s approach resonated with many African leaders and communities. In Ghana, for instance, her visit to a small business incubator highlighted the administration’s commitment to fostering entrepreneurship and innovation4.
Positive Reception
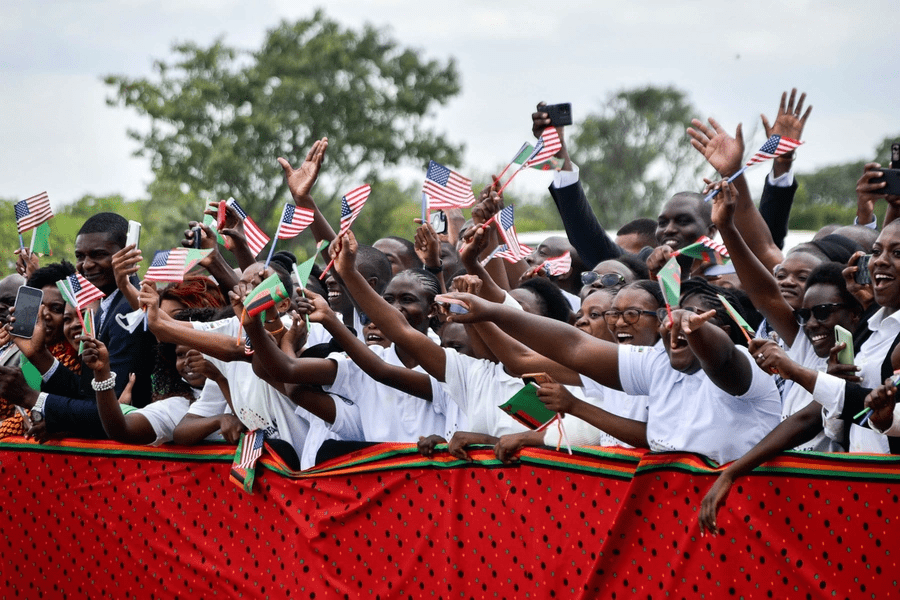
Harris’s trip generated significant interest among local populations, with crowds lining streets to witness her motorcade. As the first Black and South Asian Vice President, her visit held special significance for many Africans and members of the African diaspora. African media coverage was extensive, often outnumbering American press. This level of attention underscored the importance many African nations placed on renewed U.S. engagement with the continent.
Criticisms and Pushback
However, Harris’s trip was not without controversy. Her focus on LGBTQ rights, particularly in countries where same-sex relations are criminalized, drew criticism from some quarters. In Ghana, for example, lawmakers were debating a bill that would further criminalize LGBTQ people and their advocates3.Some critics argued that Harris’s emphasis on LGBTQ issues detracted from other pressing matters such as economic development and security. Others viewed it as an imposition of Western values on African nations.
Harris’s Response
In response to these criticisms, Harris maintained that LGBTQ rights are human rights issues. However, she emphasized that her visit was primarily focused on economic partnerships, innovation, and strengthening U.S.-Africa relations more broadly3.
Trump’s Africa Legacy: A Mixed Record of Engagement and Controversy
During his tenure as president and in the years since, Donald Trump’s approach to Africa has been characterized by a mix of limited engagement, controversial statements, and a focus on strategic competition with China. As the 2024 election approaches, it’s worth examining Trump’s record on Africa and how it might shape future U.S.-Africa relations.
Donald Trump’s presidency introduced a new era in US-Africa relations. His “America First” foreign policy shifted how the US interacted with the continent. This shift had significant effects on diplomatic ties, aid programs, and trade relations.
America First Policy Impact
Trump’s America First stance led to major cuts in foreign aid and diplomatic budgets. This hit many African nations that depended on US support. The policy focused on domestic issues over international commitments.
| Policy Area | Trump’s Approach | Impact on Africa |
|---|---|---|
| Foreign Aid | Substantial cuts | Reduced support for development projects |
| Diplomacy | Budget reductions | Decreased US presence and influence |
| Immigration | Stricter policies | Limited opportunities for African immigrants |
Controversial Actions
Trump’s presidency was filled with controversial statements about African countries. These remarks damaged diplomatic relations and drew criticism from African leaders. His efforts to cut aid programs made US-Africa ties even more complicated.
Presidential Engagement
Trump’s direct engagement with African leaders during his presidency was notably limited. He met with only two African presidents in the Oval Office during his four-year term, fewer than any of his predecessors in recent memory1. This reduced level of high-level diplomacy signaled to many that Africa was not a top priority for his administration.
Policy Priorities
The Trump administration frequently framed its Africa policy in terms of competition with China. This approach was not always well-received on the continent, with some African leaders pushing back against being treated as pawns in a great power competition
The Trump administration’s Africa strategy, unveiled in late 2018, focused on several key areas:
- Countering China’s influence
- Promoting U.S. trade and investment
- Combating terrorism
- Streamlining aid programs
Trump Administration Initiatives
Despite the challenges, the Trump administration started some initiatives for Africa. The US International Development Finance Corporation was created to counter China’s influence.
A significant policy development was the launch of the Prosper Africa initiative, aimed at doubling trade and investment between the U.S. and Africa. This program sought to leverage American private sector engagement on the continent.
Trump’s approach to Africa reflected his broader America First agenda. It put domestic concerns before international engagement, changing US-Africa relations. These changes still shape foreign policy debates today.
Controversial Statements and Actions
Trump’s presidency was marked by several controversial moments related to Africa:
- The reported use of a derogatory term to describe African nations in a 2018 meeting about immigration
- Implementation of travel bans affecting several African countries
- Proposed deep cuts to foreign aid programs, which Congress largely rejected
These actions and statements strained relations with many African nations and leaders.
Looking Ahead
Trump’s supporters suggest that a potential second Trump administration would take a more “transactional, realistic and pragmatic” approach to Africa4. This could include:
- A renewed focus on countering Chinese influence
- Emphasis on critical mineral supply chains
- Less public emphasis on democracy and human rights issues
- A more skeptical approach to public criticism of African partners
Comparing Foreign Policy Priorities
The US presidential elections spotlight foreign policy priorities. Kamala Harris and Donald Trump offer unique visions for global leadership. A recent poll highlights Harris as the top choice for the Democratic nomination in a crisis scenario.
Harris, an expert from the Homeland Security and Intelligence Committees, champions national security. She has been a strong advocate for defending allies against Russian aggression and enjoys a robust relationship with Israel’s government.
Trump’s “America First” policy has raised concerns in Europe and Asia about trade threats. His handling of Taiwan has also sparked intense debate in foreign policy circles.
Voters’ concerns mirror the complexities of global affairs. In North Carolina, 73% deem national security crucial. Nationally, preventing terrorist attacks and curbing illegal drug flows are top long-term concerns.
| Issue | Republican Support | Democratic Support |
|---|---|---|
| National Security (NC) | 42% | 30% |
| Russia-Ukraine Conflict | 36% | 34% |
The upcoming election will significantly influence America’s global stance. It will affect international alliances, trade deals, and security partnerships.
Economic Relations and Trade Agreements
The future of US-Africa economic relations is uncertain as the 2024 election nears. Trade agreements and economic partnerships will be crucial for both Harris and Trump.
AGOA’s Uncertain Future
The African Growth and Opportunity Act (AGOA), a vital part of US-Africa trade, is at a crossroads. Its renewal, set for 2025, could significantly alter economic ties. AGOA has granted duty-free access to over 1,800 African products in the US, greatly enhancing trade.
Countering China’s Economic Influence
China’s economic presence in Africa far surpasses the US. In 2021, US-Africa trade was $44.9 billion, whereas China-Africa trade hit $254.3 billion. Both Harris and Trump must devise strategies to counter China’s expanding influence.
Potential New Trade Initiatives
New trade initiatives could be vital to strengthen US-Africa economic ties. Trump’s administration preferred bilateral agreements, targeting individual countries. Conversely, a Harris administration might favor multilateral frameworks, engaging with African nations as a collective.
| Approach | Trump | Harris |
|---|---|---|
| Trade Policy | Bilateral focus | Multilateral framework |
| Import Tax | 10% on all imports | No proposed changes |
| China Strategy | Up to 60% tax on Chinese imports | Diplomatic approach |
The global landscape is evolving, offering African nations diverse investment options. As US policies change, countries aligning with US economic and security goals may discover new opportunities in this shifting environment.
Security Cooperation and Peacekeeping Efforts
The security cooperation and peacekeeping efforts in Africa are undergoing significant changes. China has notably increased its involvement, sending 1,802 military and police personnel to UN peacekeeping missions. Meanwhile, Russia’s influence is growing, particularly through the Wagner Group. This development poses a challenge to the US’s security influence in the region.
Vice President Kamala Harris’s stance on international development and security cooperation might diverge from the current administration’s. Her emphasis on racial injustice and climate change could lead to a reorientation of US priorities in Africa. However, her limited interaction with key international leaders on critical security issues has raised concerns among critics.
The US is currently facing global security threats on a scale similar to those of 1945. With geopolitical tensions escalating, including Vladimir Putin’s actions in Europe, the necessity for effective peacekeeping efforts is evident. Future US administrations will need to navigate these evolving security dynamics and possibly reassess their peacekeeping strategies in Africa.
| Country | Peacekeeping Contribution | Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| China | 1,802 personnel | UN missions |
| Russia | Undisclosed | Wagner Group |
| US | Varies | Reassessment needed |
The global security landscape is changing, requiring the US to adjust its approach to security cooperation and peacekeeping in Africa. This adaptation is vital for maintaining influence and promoting stability in the region.
Kamala Harris or Donald Trump: Who Will Be Better President for Africa
The US presidential elections are intensifying, with Kamala Harris and Donald Trump at the forefront. Their potential influence on African foreign policy and economic growth is a significant concern.
Potential Policy Shifts under Harris
At 59, Harris introduces a new outlook on US-Africa relations. Her background hints at a deeper engagement with the continent. Polls indicate nearly half of Americans believe Harris is more dedicated to democracy than Trump. This could result in enhanced diplomatic connections with African countries.
Likely Continuation of Trump’s Approach
Trump’s “America First” policy might diminish US involvement in Africa. 45% of Americans trust Trump over Harris on economic matters. This could signify a decrease in US investments in African economic projects. Trump’s campaign emphasizes domestic issues, potentially overshadowing African concerns.
Impact on Key African Issues
Harris has an advantage over Trump on racial issues and healthcare, which could benefit African nations seeking US support. Trump’s stance on trade might impact existing agreements like AGOA. The poll reveals no clear national leader, hinting at uncertain times for US-Africa relations.
| Candidate | Median Polling Average | Potential Impact on Africa |
|---|---|---|
| Kamala Harris | 53.2% | Increased diplomatic engagement |
| Donald Trump | 46.8% | Focus on domestic issues |
The Role of US Aid and Development Programs in Africa
US aid is vital for international development in Africa. USAID leads in foreign assistance, focusing on education, health, and democratic governance. These efforts aim to enhance lives and stability in partner countries.
Recent shifts in US aid priorities are noteworthy. The Biden administration boosted the aid budget, yet foreign budgets now favor other regions over Africa. This trend could impact the scale of US programs on the continent.
Human rights promotion is a central focus of US aid. Yet, internal debates over sensitive topics can occur. For instance, in 2018, disagreements over gender equality assessments in Georgia led to two reports. One included abortion references, while the other did not.
| Administration | Aid Focus | Potential Impact on Africa |
|---|---|---|
| Biden | Increased budget, traditional programs | Continued support for existing initiatives |
| Trump (Potential) | Restructuring USAID, shift in priorities | Reduced focus on gender equality, changes in aid distribution |
Future administrations will grapple with balancing domestic needs with global development goals. This delicate balance will influence the future of US aid in Africa. It will affect areas like human rights promotion and democratic governance support.
Conclusion
The potential impacts of a Trump or Harris presidency on U.S.-Africa relations present both similarities and stark contrasts.
Both candidates would likely maintain core U.S. interests in Africa, but their approaches differ significantly. Trump’s presidency would likely focus more on immediate economic benefits and strategic competition, with less emphasis on governance issues. Harris might pursue a more holistic, long-term engagement strategy, but risks alienating some African partners through a strong focus on human rights and Western values. The success of either approach would depend on their ability to balance U.S. interests with African priorities and sensitivities.
| Issue | Trump’s Approach | Harris’s Approach |
|---|---|---|
| Economic Engagement | – “Transactional, realistic and pragmatic” dealings – Focus on countering Chinese influence – Prioritization of critical mineral supply chains | – Support for renewing and modernizing AGOA – Interest in fostering cultural and creative industries – Focus on small African enterprises |
| Foreign Policy and Values | – Less emphasis on democracy and human rights – Skeptical of public criticism of African partners – Potential reduction in foreign aid | – Emphasis on democracy, human rights, and LGBTQ issues – Risk of tensions over value differences – Potential perception of imposing Western values |
| Security and Diplomacy | – Likely intensification of counterterrorism activities – Potential for reduced diplomatic engagement | – Focus on institution-building and regional partnerships – Emphasis on root causes of extremism – Continued high-level diplomatic engagement |
| Overall Strategy | – “America First” policy continuation – Focus on immediate economic benefits – Strategic competition with China | – Comprehensive, long-term engagement strategy – Emphasis on multilateralism – Elevating Africa’s role in global institutions |
FAQ
What is the current state of US-Africa relations?
Post-Cold War, Africa has often been overlooked in American foreign policy. Yet, the US remains the largest single aid donor worldwide, providing .5 billion in humanitarian aid in 2023. While the focus has been on “soft” projects like education and health, China has significantly invested in African infrastructure, committing .7 billion in 2018, vastly outpacing the US’s 7 million.
How is Kamala Harris connected to Africa?
Kamala Harris’s heritage includes Jamaican and Indian roots, and she attended Howard University, a historically black institution. Her recent visits to Ghana, Tanzania, and Zambia underscore her commitment to Africa. She aims to connect one billion people to the internet by 2030 through the Partnership for Digital Access in Africa. Her background could influence her approach to Africa-US relations.
How did Donald Trump’s “America First” policy impact US-Africa relations?
Trump’s “America First” policy sought to reduce foreign aid and diplomacy budgets. His administration created the U.S. International Development Finance Corporation to counter China’s Belt and Road Initiative. The Prosper Africa initiative aimed to boost trade and investment. Trump’s remarks on African countries led to a proposed cut in aid, which could affect support for Africa.
His re-election bid promises to continue “America First,” implement stricter immigration laws, and cut foreign aid further, potentially impacting Africa.
What are the key challenges facing US-Africa relations?
Key challenges include the need for increased infrastructure investment, countering China’s growing influence, and addressing ongoing conflicts on the continent.
How do Harris and Trump compare on economic relations and trade agreements with Africa?
The African Growth and Opportunity Act (AGOA) is set to expire in 2025, sparking concerns about its future. AGOA has provided duty-free access to the US market for over 1,800 products. In 2021, US-Africa trade was .9 billion, dwarfed by China-Africa trade at 4.3 billion. Both candidates must address AGOA’s future and develop strategies to counter China’s economic dominance in Africa, potentially through new trade initiatives.
How do Harris and Trump’s approaches differ regarding security cooperation and peacekeeping efforts in Africa?
China has expanded its peacekeeping presence in Africa, contributing 1,802 military and police personnel to UN peacekeeping. Russia has also increased its security presence through the Wagner Group. The US faces challenges in maintaining its security influence in Africa. Future administrations will need to navigate these evolving security dynamics and reassess US peacekeeping efforts on the continent.
Which candidate is likely to be better for Africa in terms of aid and development programs?
The US is the largest single aid donor globally, focusing on “soft” projects like education, health, and governance. The Biden administration’s aid budget is the highest since the mid-1980s. However, recent foreign budgets have prioritized other regions over Africa. Future administrations will need to balance domestic priorities with international development goals, potentially affecting US aid programs in Africa.







Responses